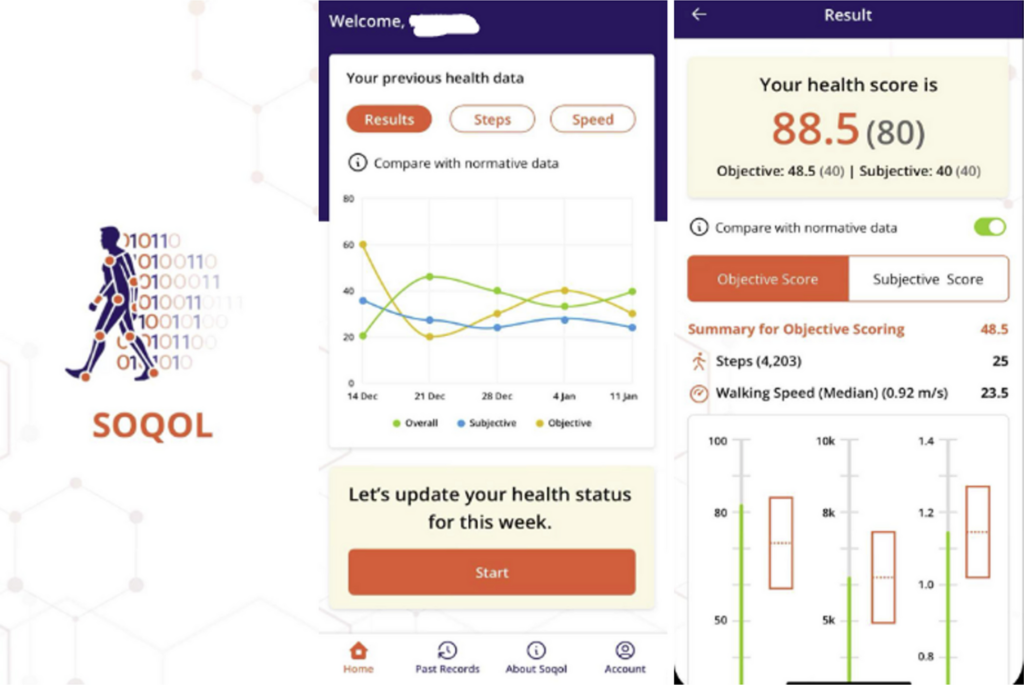
This study introduces the SOQOL score as a tool to assess health-related quality of life, combining subjective and objective health measures. Using existing data on EQ-5D-5L, step count, and walking speed, normative SOQOL data was derived. Results indicate that lower SOQOL scores with age, with women scoring lower than men. A trial in a spinal neurosurgery clinic revealed significant SOQOL deficits in surgical patients compared to non-surgical ones. SOQOL, compatible with smartphone apps, shows promise for widespread use in healthcare settings but needs further validation studies.